How to apply and when to apply phosphorus fertilizers (their names, types and compositions)
So, you've decided to figure out why and when you need to use phosphate fertilizers, or you just want to get a list of the most popular ones. You are in the right place!
Next, you will find out how important phosphorus is in plant life, what happens when it is in short supply, as well as what phosphorus fertilizers can be purchased, how to use them correctly, when and in what form to apply to the soil.

Content
Why do plants neededphosphorus
Phosphorus is one of the most important elements in the nutrition of any plant. More precisely, it is 1 of the 3 main macronutrients, which comes in 2nd place after nitrogen (on the third - potassium, on the fourth - sulfur).
What is phosphorus responsible for?
- For active root formation.
- Improves flowering, has a positive effect on fruit formation — their quantity and quality (for their large size, sugar accumulation, brighter color), and accelerates maturation... Accordingly, the main amount of phosphorus is consumed precisely in the first phases of development and growth, as well as flowering and fruit formation (i.e., in spring or in the first half of summer).
- Increases winter hardiness (frost resistance) perennials, also plants better tolerate drought.
That is why it is so important at all stages of development any plant provide phosphorus.
By the way! The presence of phosphorus also has a direct and positive effect. on nitrogen availability!
Signs of phosphorus starvation of plants
With a lack of phosphorus in plants, the following deviations in development are observed:
- Inhibited (weak) growth, in which short and thin shoots are formed.
The root grows weak. What can we talk about the active growth of the aerial part (green mass) of the plant?
- Leaves shrink, fade and acquire purple tint (sometimes even fall off prematurely), and this primarily affects the old leaves.
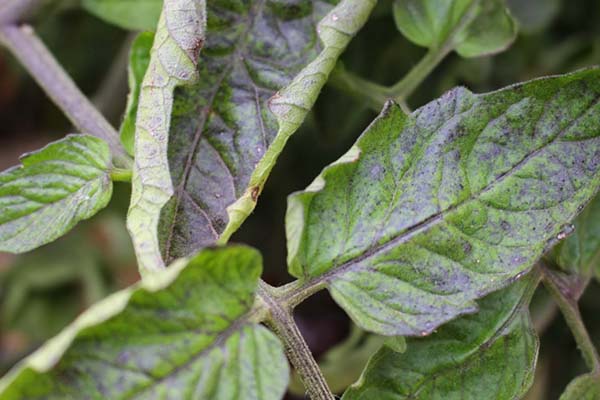

Note! How not to confuse phosphorus deficiency with sulfur deficiency?
With sulfur deficiency, the shade of the leaves does not change, and here stems and petioles acquire purple color.
- The timing of flowering and fruit formation is delayed.
- The number of ovaries decreases = yield decreases, as well as the sugar content in fruits (they cease to be sweet and aromatic).
Why it happens?
- You forgot to add phosphorus to the soil.
- Introduced, but in a form inaccessible to plants (for example, dry in spring).
- The temperature is too low (below +5 .. + 14), which is why plants, in principle, cannot consume phosphorus.
What to do?
- At the first symptoms, you need urgently add quickly dissolving and easily digestible phosphorus fertilizers to the soil (perform liquid feeding).
However! Unfortunately, the old purple leaves will no longer recover, but you can save the younger ones.
- And also it's better to do it regularly — Apply once a year in the fall dry for digging (plowing or loosening).
Interesting! It is fairly believed that the plant you can't overfeed with phosphorus, i.e. it takes from the soil only as much phosphorus as it needs.
However, it should be borne in mind that increased amount of phosphorus in the soil turns out negative impact on availability others important macro and microbatteries (potassium, zinc, boron, iron, copper).
When to fertilize plants with phosphorus fertilizers: optimal timing of application
All phosphate fertilizers, as a rule, are applied in autumn (for example, for digging, plowing or loosening)since they are very difficult and take a long time to assimilate - they take a long time to dissolve and transform into a form accessible to plants.
By the way! The site has a separate detailed article about what fertilizers are best applied in the fall to the soil for digging to restore fertility.

However, if this was not done in the fall, then in the spring you need to prepare an easily and quickly digestible phosphorus top dressing (more on this later).
Although, in principle can be made in spring, of course, efficiency will be less, i.e. the fertilizer will not start to act immediately and rather slowly, but it is better this way than nothing.
What are phosphorus fertilizers: an overview of the most popular varieties
Note! Pure phosphorus fertilizers do not exist - they always contain either nitrogen, or potassium or other meso- and microelements (most often calcium, sulfur, magnesium.
Depending on solubility phosphate fertilizers subdivided for 2 types: water soluble and almost insoluble (hard and long). The latter include bone and phosphorite meal (and the second is even more difficult to dissolve than the first).
Superphosphate
Perhaps superphosphate is the most popular phosphorus fertilizer, which comes in the following varieties:
Advice! More details about the use of superphosphate read in this article.
- plain (up to 26-29% phosphorus and 6-9% nitrogen);

- double (up to 41-49% phosphorus and 6-12% nitrogen);

Remember! Superphosphate is no not chemistry! is he made from natural minerals (apatitov), which are a natural product of geological processes (not chemical).
Other phosphate fertilizers
- Ammophos (phosphorus 52%, nitrogen 12%);

- Bone meal (up to 29-34% phosphorus, 45% calcium);
Worth knowing! Bone meal is a product pet bones processing.
It is assimilated for a long time. Most effective on slightly acidic and acidic soils (but can also be used on neutral). To increase (accelerate) the availability of phosphorus in bone meal, you can use Phosphatovite.

- Phosphorite flour (at least 22% phosphorus, 30% calcium).

Assimilated long and only on acidic soils... To increase (accelerate) solubility, it is desirable to apply together with acidic fertilizers (for example, with ammonium sulfate - 21% nitrogen).

Complex fertilizers containing phosphorus
- Nitroammofosk (all elements 16% each);

- Diammofoska (10% nitrogen, 26% phosphorus and potassium each);

- Borofosk (10% phosphorus, 0.5% boron, 20% calcium, 15% potassium, 2% magnesium).

- Potassium monophosphate (50% phosphorus and 33% potassium).
Potassium monophosphate is the most concentrated, fast-acting and easily digestible phosphorus-potassium fertilizer.
However, its price is appropriate (5-6 times more expensive than superphosphate, but also more effective).
So in November 2019, in the Leroy Merlin store, the price of 0.5 kg of potassium monophosphate is 128 rubles (i.e. 1 kg = 256 rubles), 1 kg of double superphosphate - 56 rubles, 1 kg of simple superphosphate - 44 rubles.

Organic fertilizers
Phosphorus contains in a small amount (3-6%) in almost all organic fertilizers: wood ash (up to 6% in birch and pine ash), compost (up to 2%), humus and even dry granulated chicken manure (up to 3%).

How to use phosphorus fertilizers correctly: methods and rules for their application
Phosphate fertilizers bring under the root (in the trunk circle plants), i.e. do root dressing in dry or liquid form.
Phosphates are almost not absorbed through the leaf, so foliar feeding on the leaves (spraying) does not make much sense.
With the exception of potassium monophosphate, but spraying it with a solution, as a rule, is carried out to saturate the plant more with potassium than phosphorus.
As for how best to do such a feeding - in dry or liquid form, it all depends on the purpose:
- If you need urgently feed the plant (in spring, summer or even autumn), then only in liquid form (and it is desirable to use either an instant fertilizer such as potassium monophosphate, or make special infusion of superphosphate or they also say "extract").
- If you contribute superphosphate in the fall in the calculationso that it becomes fully available to plants only next season, then, naturally, dry (for example, on a garden bed for digging or sprinkling, and then be sure to embed the granules in the near-trunk circle of a tree or shrub).
It is worth understanding! Naturally, the use of phosphorus fertilizers is allowed in the spring (when preparing the beds), with direct planting (in the planting hole), as well as for feeding during the growing season.
However, the effectiveness will be significantly lower than with autumn application or liquid feeding.

Important! See the calculated dosage for fertilizing and feeding various crops on the package (in the instructions)!
Example instructions for using simple superphosphate:
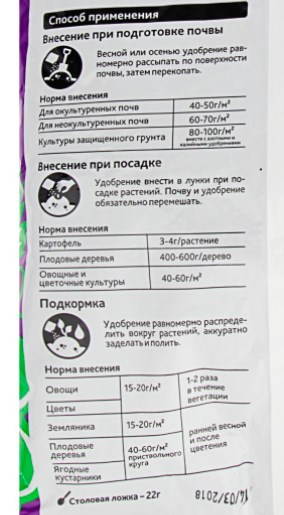
Application rules
- Phosphate fertilizers can be applied on all types of soils (optimally - on neutral), however, for example, simple superphosphate is more effective on more alkaline soils, and double superphosphate on more acidic soils (for example, slightly acidic).
- Not recommendedmix phosphorus fertilizers (the same superphosphate) from wood ashsincethis will lead to the fact that some of the phosphorus will become simply insoluble and inaccessible to plants.
- The same (undesirable use!) Applies to superphosphate together with other calcium fertilizers (or else they say calcareous, which reduce soil acidity).
Therefore, between these two processes (saturation of the soil with phosphorus and its liming, i.e., a decrease in acidity), it is necessary do an interval (at least 4-6 months, preferably a year).
- Phosphate fertilizers such as bone and phosphorite mealalthough they work best on more acidic soil, not recommended for sour crops (blueberries, azaleas, rhododendrons, hydrangeas), since they reduce soil acidity.
Well, now you know what phosphorus fertilizers are, when and how to use them in the garden and vegetable garden. Successful phosphate fertilizing!

