Reasons and what to do if tomato seedlings turn yellow
Not only novice gardeners, but also experienced gardeners are often faced with the problem of yellowing of leaves in tomato seedlings. This may be a sign of improper care of the seedlings, in particular a lack of nutrients, and also indicate the development of one of the fungal diseases. In any case, this cannot be ignored. And first of all, it is necessary to understand the reasons and promptly apply measures so that the yellowed tomato seedlings recover.
Well, let's understand and visually assess the damage!

Content
- 1 Causes of yellowing of tomato seedling leaves
- 2 Tomato seedlings turned yellow due to nutritional deficiencies (fertilizers)
- 2.1 Leaves turn yellow evenly - lack of nitrogen
- 2.2 Leaves turn yellow and dry at the edges - potassium deficiency
- 2.3 Leaves turn purple - lack of phosphorus
- 2.4 Leaves turn yellow, but veins remain green - lack of iron
- 2.5 Lack of other trace elements (manganese, zinc, sulfur and magnesium)
- 2.6 What to do if you are not sure which item is missing
- 3 Tomato seedling leaves turned yellow due to violation of growing rules
- 4 Yellowing of tomato seedlings due to diseases and pests
Causes of yellowing of tomato seedling leaves
Everyone knows that the leaves of a plant are the main indicator of their state (health). Accordingly, if there is a change in their color (yellowing), then this clearly indicates the occurrence of some kind of problem.
As a rule, one or another yellowing of the leaves of tomato seedlings occurs due to a lack of nutrition, namely, certain micro and macro elements.
In addition, tomato seedlings may begin to turn yellow due to disturbances in growing conditions (watering regime, lighting, temperature), which cause nutritional deficiencies.
Diseases and pests should also not be ruled out, but at home, seedlings, as a rule, are less susceptible to them.
By the way! If the leaves of your tomato seedlings not only turned yellow, but curled upthen about the reasons for their twisting You can find out from this material.

Tomato seedlings turned yellow due to nutritional deficiencies (fertilizers)
Everything is simple here: the appearance of the leaves, namely the specifics of yellowing, will point you to the reason for their yellowing - the deficiency of a certain nutrient, which must be replenished by liquid feeding with a suitable fertilizer or by increasing its concentration or frequency of application (if you have already applied fertilizers).
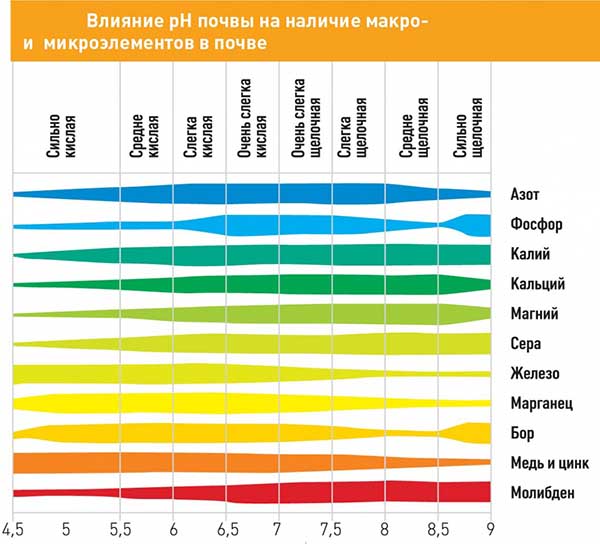
It is worth consideringthat the yellowing of the leaves of seedlings due to starvation can begin not only because of the banal lack of necessary nutrients in the soil.
- So, nutritional deficiencies are usually observed on overly acidic or, conversely, alkaline soils.
The fact is that certain nutrients bind and become practically inaccessible (difficult to assimilate) for plants at higher or lower levels of soil acidity (pH).
- Excessive or unbalanced fertilization
can also lead to the fact that some nutrient macro - and micronutrients become less available to plants. - Low temperatures, excessive compaction or excess moisture soils can also have a negative impact on the availability of plant nutrients.
Thus, for the plant to receive in abundance all the necessary macro- and microelements, food should be balanced, soil acidity - suitable (neutral - 6-7 pH), a care - right.
Leaves turn yellow evenly - lack of nitrogen
Deficiency of nitrogen nutrition is the most popular reason yellowing of the leaves of tomato seedlings.
In the case of nitrogen starvation, a general yellowing of the leaf plates of the plant (the oldest lower leaves) occurs first, and then the plant as a whole begins to lag behind (slow down) in growth.
Note! If this is a lack of nitrogenthen the leaves of tomato seedlings turn yellow evenly, a not spots, streaks or around the edges).
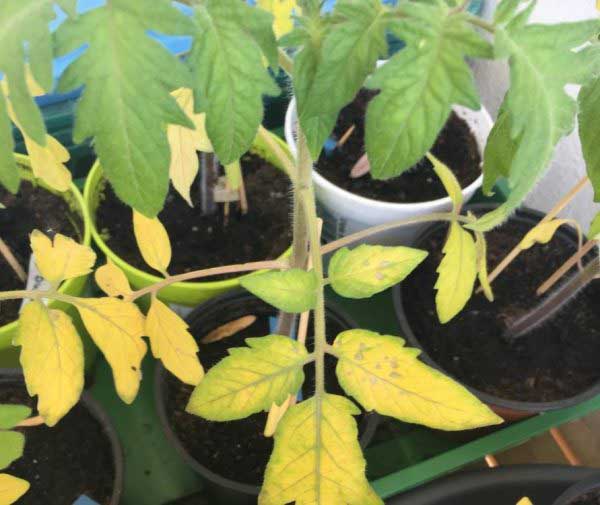

Obviously you need to do feeding one of nitrogen fertilizerswhich are:
- mineral: ammonium nitrate, urea (carbamide), ammonia solution (ammonia) other;
- organic: herbal infusion, mullein solution, chicken droppings.
Leaves turn yellow and dry at the edges - potassium deficiency
If this is a lack of potassium, then in this case the leaves of tomato seedlings will turn yellow exactly their tips (a yellow border is formed),
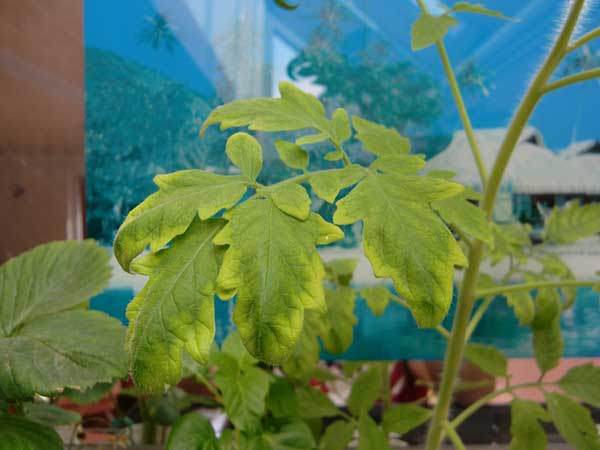

and then a peculiar marginal burnbut at the same time central part of the leaf will remain green.

Tomato seedlings can be root-fed with one of the following potash fertilizers:
- Mineral: pure potash - potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate), or complex - potassium magnesium (+ magnesium), potassium nitrate (+ nitrogen), potassium monophosphate (+ phosphorus). The latter can be fed directly on the leaves (i.e. sprayed).

Important! In no casedo not use chloride fertilizers: potassium chloride or potassium salt.
- Organic - wood ash (+ phosphorus, calcium and other trace elements).
Worth knowing! Excessive application of wood ash can block the absorption of calcium and magnesium, therefore, the solution should be added with acetic acid.

Leaves turn purple - lack of phosphorus
Note! With a lack of phosphorus, the leaves of tomato seedlings turn purple (turn blue)... No yellowing occurs.

Leaves turn yellow, but veins remain green - lack of iron
Perhaps, second most popular the reason for the yellowing of the leaves of tomato seedlings is a lack of iron. The fact is that iron deficiency has the strongest effect on reducing the content of chlorophyll in leaves. Therefore, very often "chlorosis" is used by many as a synonym for "iron deficiency".
Symptoms of iron deficiency (interveinal chlorosis of plant tissues) are yellowing of the upper young leaves of seedlings, in which veins remain dark green and also there is a strong inhibition of plant growth.

In this case, you need to do exactly easily and quickly assimilated feeding tomatoes with iron, i.e. in chelated form, since the lack of iron is most often due to the reduced mobility of iron in the plant.
For this, it is optimal to carry out foliar feeding seedlings over the leaves (sprinkle) xiron iron.

Or use a similar drug Ferovit.

Important! Iron vitriol is a fungicidal agent that is not used for feeding to replenish iron deficiency.
Lack of other trace elements (manganese, zinc, sulfur and magnesium)
- a lack of manganese characterized by the emergence small light yellow spots on the leaves (which then turn brown and die off), while the veins remain green (as is the case with iron deficiency). Stronger manifested on old lower leaves.

You need to feed your tomatoes manganese sulfate (But not potassium permanganate, which is called "potassium permanganate"!).
Note! It is better to add all trace elements on the sheet, i.e. spraying (foliar top dressing).

- Disadvantage zinc it is also often the cause of chlorosis = yellowing of the leaves of tomato seedlings, proceeding similarly to a deficiency in manganese, however, the spots in this case turn orange-brown.

Zinc sulphate - this is what you need to feed the tomatoes (spray).

- With a shortage sulfur more old leaves (according to other sources, on the contrary, young) acquire light green color, while the veins themselves also turn yellow.

To replenish the sulfur deficiency, you need to feed ammonium sulfate (+ nitrogen).

- When lack of magnesium leaves turn yellow between veins (in the interveinal space), and first old bottom, and then the younger upper ones, subsequently they necrotic.

- Obviously, the plant needs a magnesium supplement - magnesium sulfate.

What to do if you are not sure which item is missing
And still it is quite difficult to determine the deficiency of a certain (specific) trace element, for example, in contrast to the lack of nitrogen or potassium (although there may be doubts). Therefore, in order not to torment yourself and your seedlings, it is optimal to carry out complex feeding with full micronutrient fertilization, for example, Humate +7, and the plant will take what it needs.

Cytovit is also suitable, in which, in addition to microelements, there are also small amounts of macroelements (nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus).

It is even more convenient to use specialized complete complex fertilizers, which include all the necessary food elements (macro and micro). For example, this is Fertika Lux.

Agricola for tomatoes, peppers, eggplants and similar.

Tomato seedling leaves turned yellow due to violation of growing rules
If you improperly care for your tomato seedlings, do not follow the rules of its maintenance and make mistakes in care, this can also affect the color of its foliage from green to yellow.
By the way! On the site you can find material on proper care of tomato seedlings at home.
Watering and moisture
Rare, as well as poor watering (not abundant enough), can lead to the fact that tomato leaves begin to wilt, turn yellow and dry out (dry out) from lack of moisture.
In the same time excessive soil moisture, moisture stagnation due to poor drainage can lead to root damage, a decrease in their ability to absorb nutrients from the soil, and as a result, to yellowing of the leaves of seedlings, reduced growth energy and its wilting.
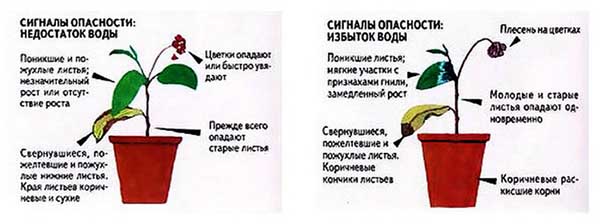
Dry air
Low air humidity can also cause wilting and yellowing of tomato leaves.
Temperature
On the contrary,excessively high temperature (over + 30..35) can cause wilting and twisting of leaves of seedlings, as well as edge necrosis of leaves.
Short daylight hours or sunburn
Due to lack of solar energy (too short daylight hours) in the leaf system of the plant, the processes of photosynthesis are suppressed, the leaves of tomatoes begin to become paler, and the seedlings themselves stretch out (reach out for the light).

therefore do not sow tomatoes too early for seedlingswhen the daylight hours are still not long enough (less than 12 hours), or it is necessary to independently illuminate with special lamps.

Also, plants may lack light due to excessive thickening of crops.
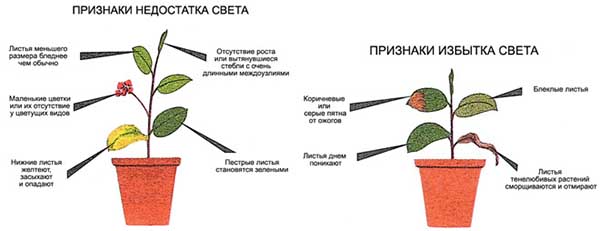
On the contrary, if your seedlings are on south windowsillthen in direct sunlight its leaves can receive sunburn... Including due to the ingress of water droplets when watering the plant.
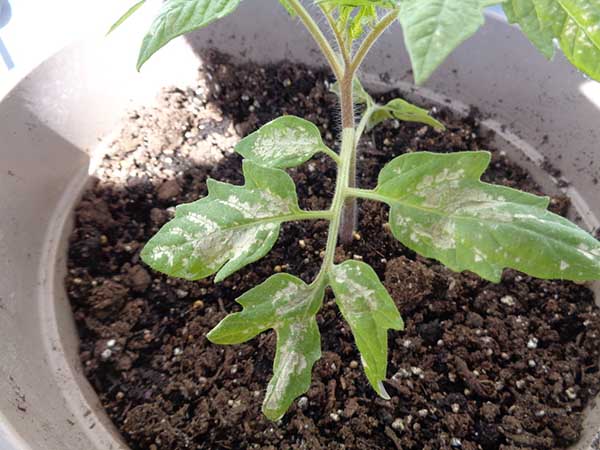

Important! In both cases (with a lack and excess of light), the leaves of the seedlings rather turn white and dry than yellow.
Bad priming
Poor-quality and unsuitable soil can cause a slowdown in the growth of seedlings and the appearance of a yellow tint of foliage.
So, for example, if the substrate was prepared without adding a baking powder (sand or perlite), then this can lead to the fact that after each watering, the soil in the pot strays into a solid heavy ball, and this does not allow the roots to develop.
If the soil is not loose (not air- and moisture-consuming), then again this can cause suffocation of the roots, due to which they will not receive the required amount of oxygen.
Seedlings are too crowded in seedling containers
Often, seedlings stop growing due to the fact that its root system has already mastered the entire feeding area and has outgrown the planting capacity, which is why it simply does not have enough space for further growth and development.
It is obvious that you delayed with picking tomato seedlings into new, larger containers.
Unsuccessful transplant (picking)
Often enough sloppy and poorly executed pick (transplanting plants into separate containers) causes the leaves of tomato seedlings to turn yellow, during which you damaged the root system, due to which the plant cannot normally receive nutrition.
Therefore, after picking, seedlings are desirable feed with one of the rooting and growth stimulants to relieve plant stress (for example, Kornevin, Zircon or Epin).
By the way! The site has detailed articles about the correct picking of tomato seedlings.

After planting in the ground (on the garden)
Often, tomato seedlings turn yellow immediately after planting in open ground. For example, this may be due to the fact that you did not adapt the plants to environmental conditions (did not harden them), planted them in unheated soil, or there were recurrent spring frosts.
Note! As a rule, after planting seedlings in the ground (open or closed), various diseases and pests begin to attack the tomatoes, which is also evidenced by a change in the normal color of the foliage. Read more about this in the next paragraph.
Yellowing of tomato seedlings due to diseases and pests
The most common disease of tomato seedlings is blackleg, about the reasons and preventive measures of which you can read in the relevant article.

Other diseases of tomatoes, one way or another leading to yellowing of the leaves, appear, as a rule, after planting seedlings in open ground or a greenhouse.
For example, brown spot (cladosporium) of tomatoes characterized by the following manifestations (symptoms):
- On the leaves during the flowering period, pale yellowish (rather white than yellow) spots are formed on their upper side, and a light bloom of mycelium appears on the lower (inner side).
- Gradually the spots turn dark brown, velvety, and then affected leaves dry out, curl up and fall off.
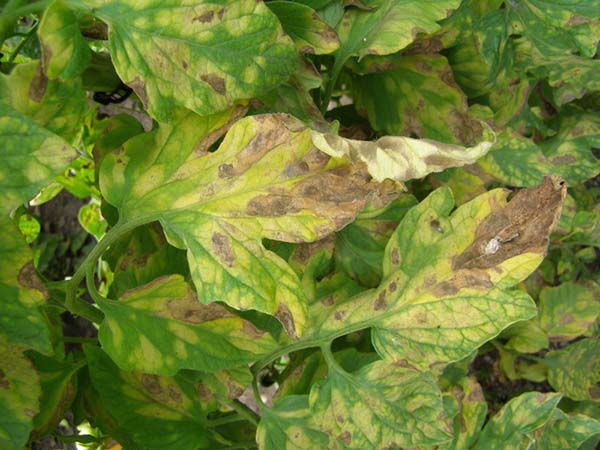

If, nevertheless, you find the first signs of brown spot, then immediately start spraying the plants with a solution of copper oxychloride (40 g per 10 l of water, 1 time in 10-14 days) or a biological preparation Fitosporin (according to instructions) or Trichoderma Veride (Trichodermin).
Also needed manually pick off all leaves affected by brown spotso that the disease does not spread.
When late blight of tomatoes leaves usually do not turn yellow, but downright burn out (turn brown and dry), but the disease is very, very serious, and most importantly - widespread.
Advice! About, how to deal with late blight on tomatoes, read in this article.
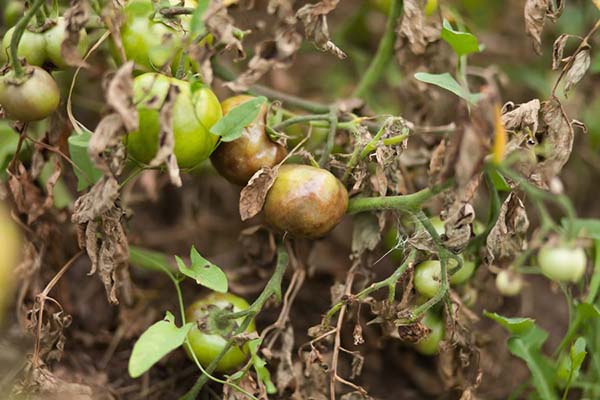

In the worst (terrible) cases, the yellowing of tomato leaves can be caused by:
- leaf roll virus (yellow curl in tomatoes);

- bacterial cancer.

There is nothing you can do about it, you just need to quickly remove the affected bushes.
Attack whiteflies for greenhouse tomatoes causes the leaves to turn yellow, dry out and fall off. However, the first signs of the presence of this pest are the formation of shiny white spots (white bloom) on the leaves.

By the way! The site has a separate material about how to get rid of whitefly on tomatoes in a greenhouse.
Well, the reasons for the yellowing of the leaves of tomato seedlings, as well as what to do in each of the specific cases, you know. This means that you yourself will be able to determine in time what needs to be done. Good luck!


Thanks for the advice, as a novice gardener, the information was very useful to me, I found the answer to my question.
Very helpful article. Last season I had such problems. Now I realized that there was an excess of phosphorus in the soil.
Thank you! Very detailed and understandable information. I especially liked the photo with the description. Now I will know how everything looks clearly.