Planting sweet pepper seedlings in a greenhouse and open ground: terms and rules
Your seedlings have grown, they can't wait to be in the ground in your garden (or greenhouse). And so you asked the question: "When to plant seedlings of peppers in a garden in a greenhouse and open ground?"
Next, we will consider this and other related questions regarding the optimal timing, choice of location and preparation of the garden, as well as how to properly plant pepper seedlings in a permanent place in open or closed ground.

Content
- 1 When to plant pepper seedlings in open ground and a greenhouse: optimal timing
- 2 Choosing a place and preparing a bed for growing pepper
- 3 Preparing pepper seedlings for planting in the ground: hardening
- 4 Planting pepper seedlings in open ground or greenhouse
- 5 Further care of pepper in the greenhouse and open field: growing rules
When to plant pepper seedlings in open ground and a greenhouse: optimal timing
Planting pepper seedlings in a permanent place should only be when the threat of recurrent spring frosts will pass.
Important! Ignoring the favorable temperature conditions for planting seedlings can lead to hypothermia of seedlings, stunting, diseases, which will negatively affect the future harvest, which in the end may not be. In the case of spring frosts, the seedlings may die altogether.
Note! Peppers can withstand temperatures as low as +5 degrees.
The average daily air temperature should be stable above +13 .. + 15 degrees.
Wherein the soil by this time should warm up to + 10-12 degrees, and even better up to + 12-15 degrees (allowed if the soil temperature at the planting depth is not lower than + 10-12 ° C).
Important! Late transplanting of seedlings is also undesirable, as it falls into a period when temperatures rise sharply, and the yield decreases due to a shorter growing period.

The depth of heating should be 1/2 of a shovel bayonet (10-15 cm), in other words, this is the depth of the landing hole. At about this depth, you should place a thermometer in the ground to find out its temperature.
Naturally, if you are going to initially plant seedlings of peppers under a film in an arc greenhouse, then this can be done a little earlier, about 5-7 days.
And planting pepper seedlings in the greenhouse is carried out even earlier (by 10-14 days), because the soil in closed ground warms up much faster.
In different regions
Of course, depending on the climatic characteristics of your region of residence and the current weather conditions, the timing of planting pepper seedlings in open ground may vary, but approximate dates can still be called:
- In the South of Russia - this is the second half-end of April;
- In the Central zone (Moscow region) - the second half of May;
And in the greenhouse can be planted at the end of April or in the 1st decade of May, i.e., as already mentioned, 10-14 days earlier.
- In the North-West (in the Leningrad region) - early June;
- In the Urals and Siberia - not earlier than 3 decades of May - early June.
Choosing a place and preparing a bed for growing pepper
Sweet peppers grow well and bear fruit in light, permeable and well-warmed soil, which means that a well-lit place for planting it should be chosen - the sunniest in the garden.

Advice! It is ideal if the garden bed is protected from drafts on the north side.
After which it is better to plant: crop rotation rules
As for what is better to plant pepper after, then best predecessors are:
- siderates, especially cereals (rye, vetch);
- legumes (beans, peas);
- pumpkin crops (cucumbers, pumpkin);
- cabbage.
In addition, it is quite possible to plant it after carrots, beets, as well as onions and garlic.
Worst predecessors, after which it is not at all desirable to plant peppers - all nightshades (eggplant, potatoes, physalis and the pepper itself).
Due to the observance of the rules of crop rotation, the possibility of contamination of the crop with diseases that could remain in the soil is excluded.
Thus, if you want to get a good crop harvest, then every year you need to either find a new place for planting peppers, or carefully remove the entire topsoil and fill it with new fertile soil, or be sure to disinfect and apply a good portion of fertilizers.
Preparing the garden
Since pepper is a very thermophilic culture, it is perfect high (warm) beds in which the soil warms up faster.
Garden bed for peppers (and other cultures) it is always advisable to cook in advance, even with autumn... To improve its fertility for digging (on the bayonet of a shovel), you should make phosphoric and potash fertilizers (superphosphate, potassium sulfate - 20-40 g per 1 sq. m, or wood ash - 100-200 gr.per 1 sq.m.).
Nitrogen fertilizers (urea or ammonium nitrate - 15-30 gr. per 1 sq.m.) it is worth adding already in the spring, during repeated plowing, 1/2 bayonet of a shovel (one month before landing).
Also, do not forget humus or compost (5-8 kg per 1 square meter, depending on the fertility of your soil).
3-7 days before disembarkation is very good disinfection soil by spilling it with solution Fitosporin.
You can also put 1-2 tablets of Glyocladin in the soil (deepen) not far from each bush immediately after planting.
At about the same time (in a week), so that the soil warms up faster, you can cover with foil or a white non-woven cover material.
In the next video, you can get acquainted with an even more intricate preparation of a bed for peppers.
Video: preparing a garden for planting peppers and eggplants
Preparing pepper seedlings for planting in the ground: hardening
Since the seedlings were grown at home = "greenhouse" conditions, before planting seedlings in open ground, they should first be adapted to more severe environmental conditions (for example, to sudden temperature changes, direct sunlight, etc.) so that after transplanting it does not get into a severe stressful situation.
To do this, 10-14 days before planting the seedlings in a permanent place - in open ground, you should begin to prepare it, in other words, to harden it.
First, you can simply open a window or window (to reduce the air temperature, but not lower than + 10-14 degrees). Then put the seedlings on a balcony or loggia in direct sunlight, or even better in a greenhouse or outside (on the porch).

Important! The time spent in "stressful" conditions should be increased gradually, starting from 30 minutes and up to a whole day.
Thus, this procedure will help to strengthen the immunity of plants, to adapt them to more severe external conditions.
Appearance of seedlings ready for planting
As for the requirements for appearance, the pepper seedlings by the time of planting should be:
- strong and healthy (hardened);
- with a well-developed root system;
- 20-25 cm high;
- have 6-12 true leaves.

In addition, early cultivars should have pronounced first-formed buds.
Planting pepper seedlings in open ground or greenhouse
So, let's get down to business - to planting in the ground, and first we will analyze the possible schemes for planting pepper.
Landing scheme
The optimal planting scheme for tomato seedlings depends on the strength of your plant's growth. Between the rows, as a rule, there should be at least 70, and better - all 80-90 cm:
- 40-45 cm for tall;
By the way! Tall peppers are usually grown in greenhouses.
- 30-35 cm for medium-sized;
- 20-25 cm for undersized.
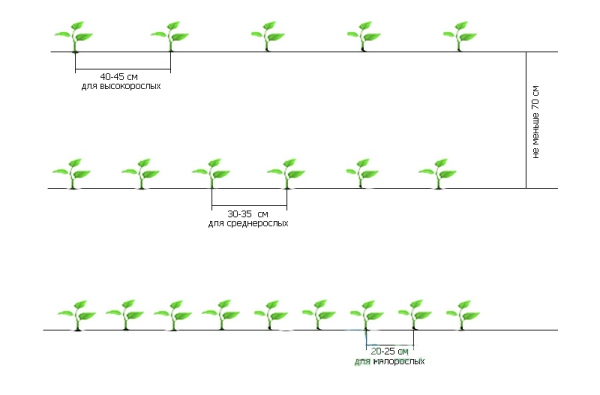
But you can also plant in a checkerboard pattern, in 2 rows (more precisely, rows), while the distance between the rows should be at least 40 cm, and preferably 50-60 cm.
Recommendation! For a more accurate planting pattern for peppers, see the back of the seed package.
Direct Disembarkation - Step-by-Step Guide
As for the time, it is best to choose either cloudy weather for planting seedlings of peppers, or in the afternoon, in the late afternoon, when the sun will set.
Step-by-step instructions for planting pepper seedlings on a garden bed in open ground:
- Prepare the garden bed in the fall, or do it in the spring.
- Determine when it will be possible to plant.
- Prepare seedlings - harden.
Advice! In order for the roots of seedlings to remain completely intact, the earthen lump should be watered about an hour and a half before planting the seedlings on the garden bed. If you cannot reach the plant, then a cardboard or plastic cup can be easily cut with scissors. And if your seedlings grew in peat cups (not cardboard), then you don't need to take them out at all.
- Dig holes and add fertilizers to them (if not already done).
For example, you can pour humus or compost into the hole, and also add a little superphosphate (3-4 grams per hole) and mix thoroughly with earth.
For disinfection and protection of pepper from diseases, you can put 1-2 tablets of Glyocladin in the hole, or even better, bury it 1-2 cm into the soil at a distance of 4-5 cm from the plant.
- Spill lightly with water.
- Transfer the seedling into the pre-prepared planting holes (to the same depth at which the plants grew in seedling containers), preserving the integrity of the earthen coma.
Important! It is believed that in no case should the root collar be buried (located where the uppermost lateral root departs), otherwise it can provoke the development of many dangerous diseases, the same black leg.
However, if the seedlings are very elongated, they can be buried along the cotyledons.

- Compact the soil next to the seedling and sprinkle with loose earth.
- Spill abundantly with water (2-3 liters per plant). If the earth settles, then sprinkle it.
- If desired, gently mulch with, for example, hay or straw. You can also use forest floor.
Video: planting seedlings of peppers in open ground
If you are planting in open ground and you are not sure that the weather has stabilized and there is a possibility of recurrent frosts, then it is better to play it safe and put a greenhouse on arcs.

Video: planting sweet pepper seedlings in a greenhouse
Further care of pepper in the greenhouse and open field: growing rules
Advice! And about that how to properly care for and grow peppers in a greenhouse, described in detail in this article.

Thus, thanks to the timely and correct planting of pepper seedlings in open ground or a greenhouse, you will lay a good foundation for future abundant fruiting and a high yield. Good luck!
Video: when and how to plant bell peppers

